Site Tools
User Tools
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
What is the data model?
The data model is a structure of data composed to represent the reality we want to vectorize. In the data model lay all the information we want to get at the end of our work. It sorts the data of the same nature together in layers. Seeing that fact, the more intricate a project is the more layers you shall have. Those layers may represent 3 types of geometries:
- points
- lines
- polygons
Practical case
In the subsequent case we will follow the realization of a new project. It is the hazard study of an area. We want to vectorize them properly. After analyzing them thoughtfully we can divide them in 3 different layers:
- A line layer containing information of the protective structures.
- A polygonal layer containing information of hazards
- A polygonal layer containing information of intensities
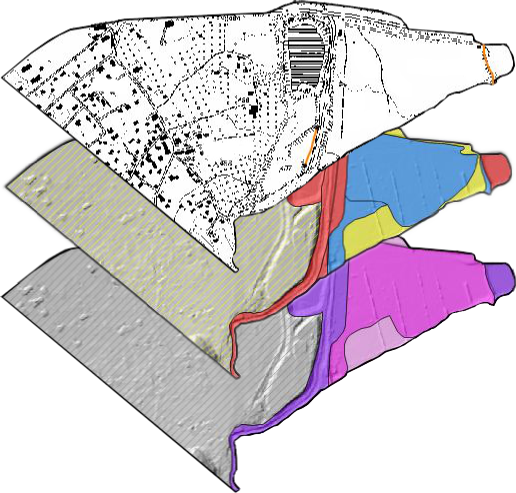
Those are the information we choose to vectorize. To do that we will need a different layer for each map; meanig two polygonal layers and a line layer. Each color of the polygonal layers represent a different object. Each object can then have individual properties. Those properties are described by the attributes. For exemple a medium hazard (object) can stem from an innondation or a Debris flow event (attributes).
All the objects can then be illustrated the following way:
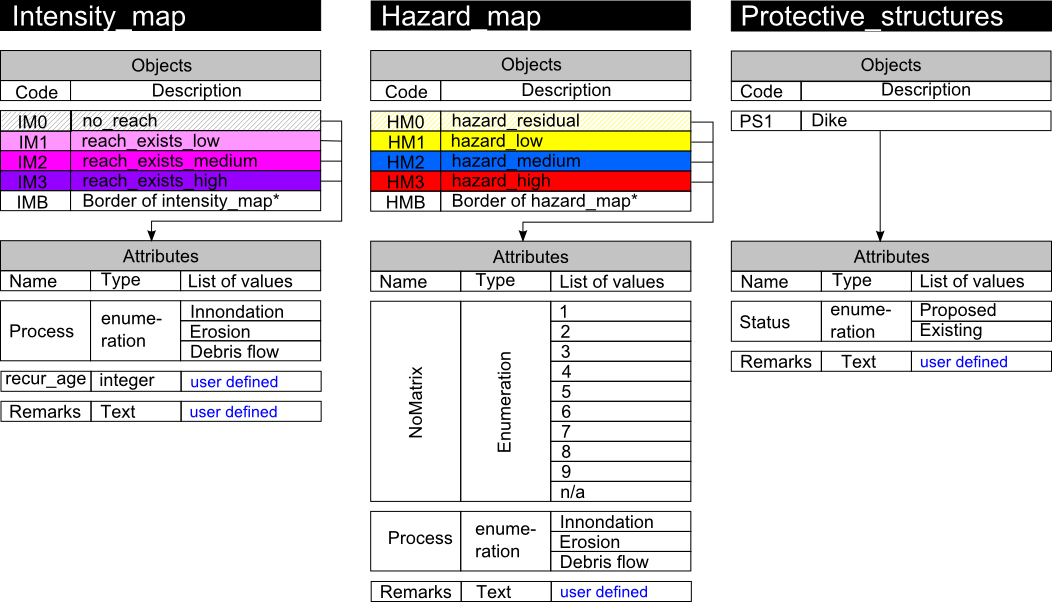
Every layer is built to satisfy the necessities of the project. It means that to work with ToolMap efficiently you have to previously analyze your data to define what your final objective is so you can easily generate your data model.
Implementation in ToolMap
Once your data model is defined, meaning it describes adequatly all the data you want to digitize, you will have to implement it into a ToolMap project. Launch ToolMap for getting started.
First of all you need to create a new empty project.
Project → New project → Empty...
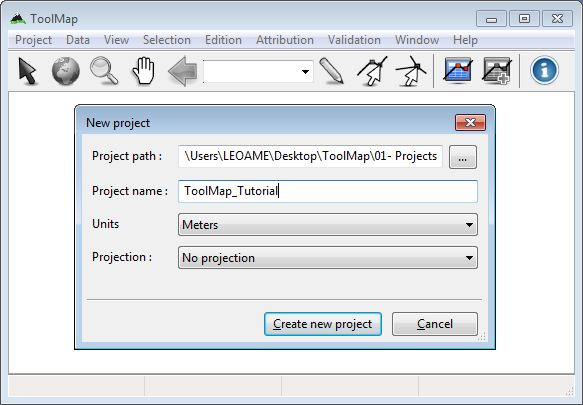
After clicking on the [Create new project] button the Project definition window pops up. On the Project properties tab set the name of the author and some comments if wanted. The spatial model tab allows you to implement your data model.
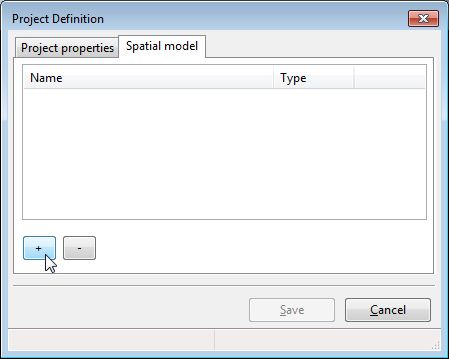
The spatial definition tab lists all the layers defined in your project. At this particular moment it is empty, but you will fulfill it with the layers you imagined as your data model.
Click now on the [+] button to add your first layer…
The Thematic layer definition window pops up. You will have several operations to do:
- Set the name of your layer
- Define its geometrical nature
- Create the objects contained in this layer
- Create the attributes characterizing the objects
The objects are listed on the first tab of the window. Click on the [+] to create a new object. Set a code and a name for every object.
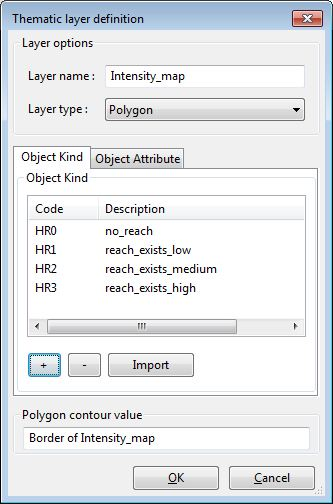
The attributes are listed on the second tab of the window. By clicking on the [+] button i can add a new attribute.
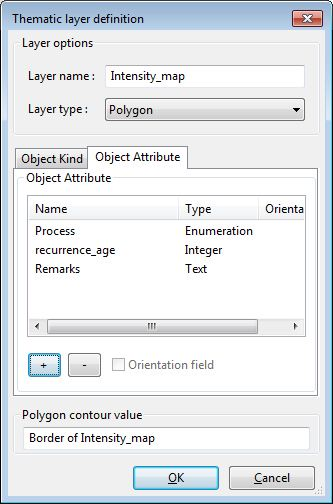
For every attribute I create I've got to define:
- The name of the attribute
- The type of the attribute
- Enumerations: define the list of value
- Text: define the maximal number of autorized characters
- Integer: -
- Float: define the field precision, field scale and the result sample.
- Date: -

Once I computed every information I can save my layer to go back to the Project definition window and create with the same process every layers I need.
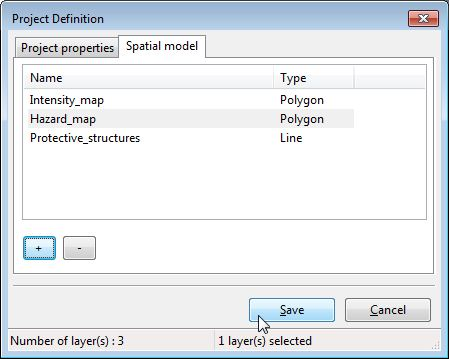
Now that my data model is fully implemented I finish the creation of my project by clicking on the [Save] button.

